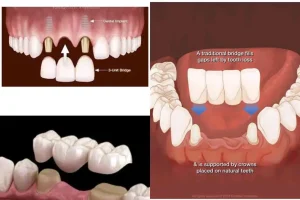
Dental Bridges
Dental bridges replace missing teeth. They can restore chewing function, enhance your appearance and improve your oral health. A dental bridge consists of crowns (that fit over your natural teeth on either side of the space) and artificial teeth (that “bridge the gap” in your smile).
What is a Dental Bridge?

A dental bridge serves as a solution for missing teeth, capable of replacing one tooth or a series of missing teeth. Essentially, it acts as a literal “bridge” to fill the gap in your smile. Custom bridges can be created by dentists to match the natural shade of your teeth.
Components of a Dental Bridge:
There are key components that make up a dental bridge:
- Abutments: These structures support the dental bridge, commonly referring to natural teeth, but can also include tiny connector posts used in implant-supported bridges.
- Pontics: These are artificial teeth that fill the gap left behind by missing teeth.
Depending on the situation and the type of bridge, it might consist of one or more abutments and one or more pontics.
Types of Dental Bridges:
Dentists employ various types of bridges based on oral health goals, including:
- Traditional Dental Bridge: The most common type, featuring dental crowns on both ends with pontics in between, bonded to healthy natural teeth on either side of the gap.
- Cantilever Dental Bridge: Similar to a traditional bridge, but with a crown on one end, used when natural teeth are only on one side of the gap.
- Maryland Dental Bridge: Uses metal wings instead of crowns to secure the bridge, typically employed for replacing front teeth.
- Implant-Supported Bridge: Rests on dental implants instead of natural teeth, suitable for cases with three or more missing teeth in a row.
Type of Bridge:
Various factors, including age, the number of missing teeth, gap size, condition of adjacent teeth, presence of natural teeth on both sides, overall oral health, and personal preferences, are considered by dentists to determine the type of bridge needed.
Procedure Details:
The dental bridge procedure varies based on the type:
- Traditional or Cantilever Bridge Placement:
- Local anesthesia is administered for comfort.
- Abutment teeth are reshaped.
- Dental impressions are taken and sent to a laboratory.
- A temporary bridge is placed until the final bridge is ready.
- Final bridge bonding occurs during a second office visit.
- Maryland Bridge Placement:
- Teeth are prepared for metal wings.
- Dental impressions are taken and sent to a laboratory.
- Final bridge bonding involves applying dental etch and using dental resin cement.
- Implant-Supported Bridge Placement:
- Involves multiple office visits, including surgery to place dental implants.
- Healing and integration of implants with the jawbone take several months.
- Final bridge placement occurs after integration, involving attachment to dental implants.
Risks/Benefits of Dental Bridges:
Advantages:
- Natural-looking solution for tooth loss.
- Restoration of chewing and speech functions.
- Prevention of neighboring teeth shifting.
Disadvantages:
- Vulnerability to damage if abutment teeth weaken.
- Risk of fracture if abutment teeth lack sufficient strength.
- Potential for gum inflammation or cavities without proper cleaning.
Recovery and Outlook:
Recovery time varies, with teeth and gums healing in one to two weeks on average. Dental bridges last five to 15 years on average, requiring replacement when signs of wear or damage appear.
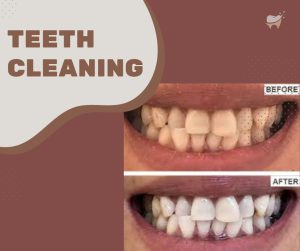
Care for Dental Bridges:
Proper care involves daily brushing and flossing, using nonabrasive fluoride toothpaste, cleaning underneath the bridge, avoiding hard or chewy foods, and regular dental checkups.
When to Call the Dentist:
Schedule an appointment if the bridge is loose or cracked, experiencing pain while chewing, or developing sensitivity or bleeding gums.
Common Questions:
- Dental Bridge vs. Implant: Which is Better?
- Implants generally last longer and preserve bone, but individual preferences and needs vary.
- Ideal Age for a Dental Bridge:
- Generally not recommended for those younger than 17 or 18, but exceptions exist.
- Number of Teeth on a Bridge:
- Typically replaces one to three teeth, with longer bridges requiring more support.
- How Long to Wait for a Dental Bridge:
- Replace missing teeth promptly to prevent shifting; however, extraction may require a waiting period for healing.
- Is a Dental Bridge Painful?
- Local anesthesia is administered during the procedure to ensure comfort.
- Do Bridges Feel Like Real Teeth?
- Adjusting to a new bridge takes time, but it eventually feels similar to natural teeth.
- Can a Dental Bridge be Removed and Recemented?
- Depends on the situation; loose bridges can often be recemented, but removal for other reasons may lead to replacement.
Read more: How Much Does a Dental Bridge Cost in Uganda?
Importance of Dental Bridges:
Missing teeth impact your smile and function. Dental bridges provide a comfortable and affordable solution for those missing one to four teeth, offering a viable alternative to partial dentures and implants. If you’re facing tooth loss, consult your dentist for personalized replacement options.

One Response